Service Lifecycle
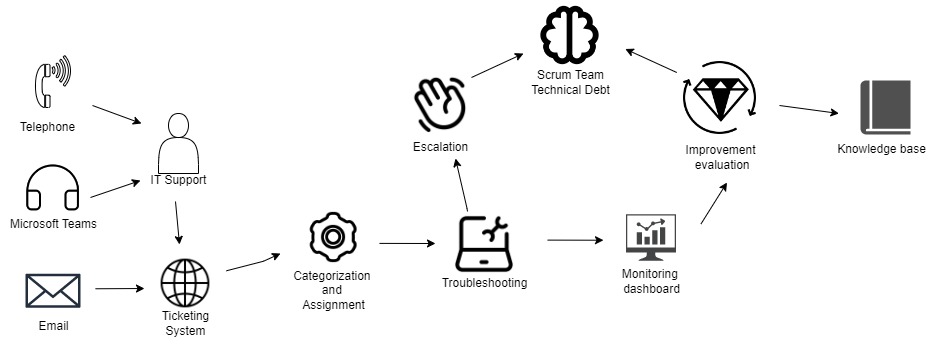
The process begins with receiving the ticket in the service channel. This can be done automatically via email and the ticket goes to the platform Jira. Or it can be created manually from Microsoft Teams meeting or phone call information by the developer. After this, the ticket should be managed in two sub-categories - maintain attributes and ticket assignment. There are different attributes that a person can assign to the ticket, for example, requestor group, ticket categories, due date, topic/tags, location, priority level, status, and issue type. During the ticket assignment, the person will assign to a task based on ticket categories. If the ticket can not be solved in 2 days, it will escalate to the second level of support which is the Scrum team and it will go to the Technical Debt section. The next step is monitoring - a dashboard will store the information and it will provide an analysis of the process. This will evaluate the process in the end and the team can use this information to improve themselves. Also, the information gathered will be stored in the knowledge base and the client can use this information to solve the ticket. The software for ticketing will be the Jira service management tool.
Last updated